What is a One-Way Clutch Bearing?
What is a One-Way Clutch Bearing?
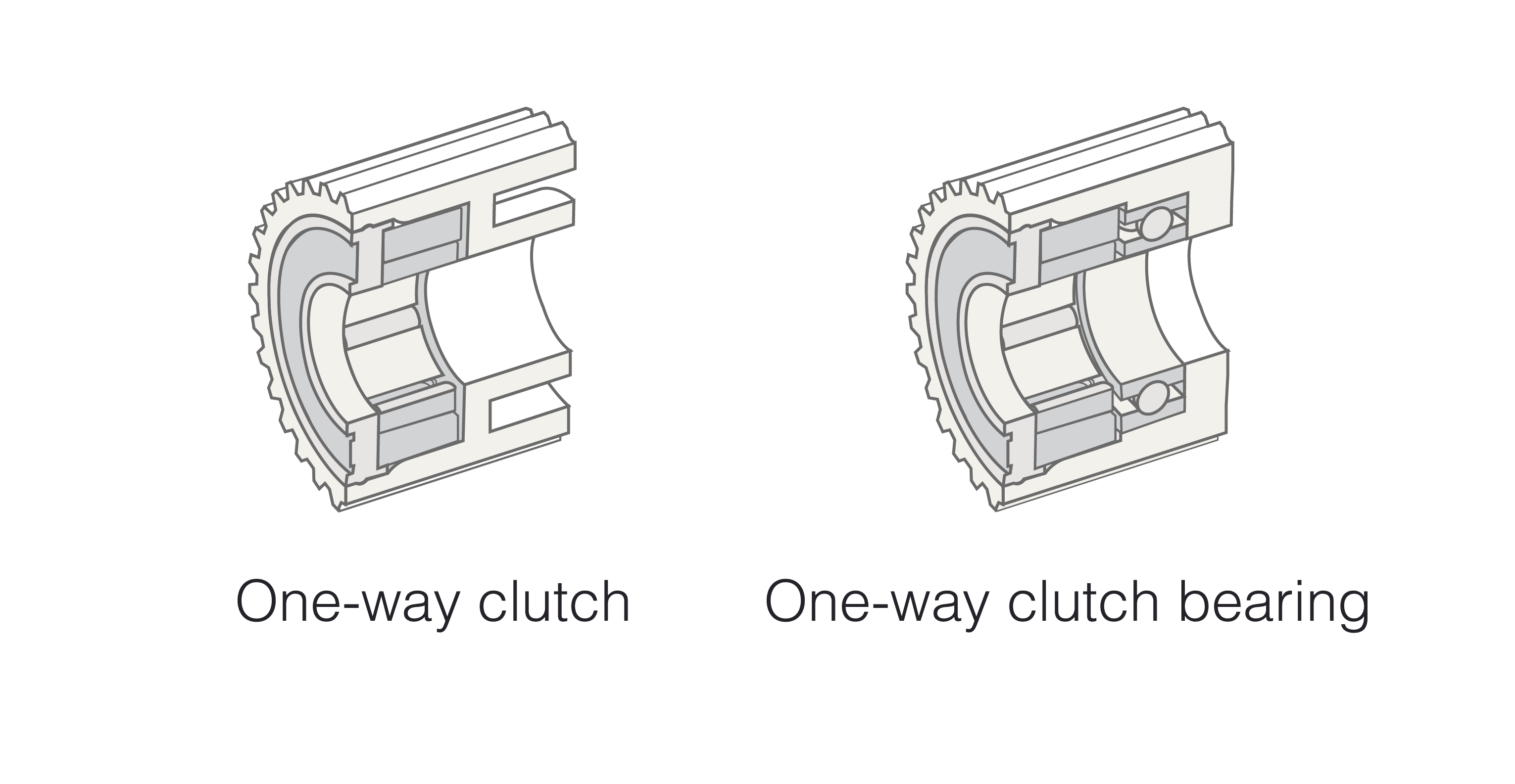
A one-way clutch is a mechanical component that, as its name suggests, transmits power in only one direction. Among these, the “one-way clutch bearing” refers to a type featuring an integrated structure combining a one-way clutch and a bearing. In other words, while it is a type of one-way clutch, its defining characteristic is that it also incorporates bearing functionality. This article clearly explains the mechanism of one-way clutch bearings and technical points such as why bearings are built into one-way clutches.
 A one-way clutch bearing mechanism and features of TOK products
A one-way clutch bearing mechanism and features of TOK products
One-way clutches and one-way clutch bearings operate on essentially the same principle. A one-way clutch features a mechanism that locks in one direction using needle pins or cams. Conversely, a one-way clutch bearing combines the mechanism of a one-way clutch with bearing functionality, enabling not only one-way power transmission but also simultaneous shaft support.
TOK's one-way clutches also fall into this “one-way clutch bearing” category. The bearings integrated into TOK's one-way clutches use plastic sliding bearings, making them less likely to damage the mating shaft and enabling smooth operation. Furthermore, we can also deliver them combined with ball bearings tailored to the application conditions. This allows us to provide optimal performance suited to the specific application.
 Why is a bearing integrated into the one-way clutch?
Why is a bearing integrated into the one-way clutch?
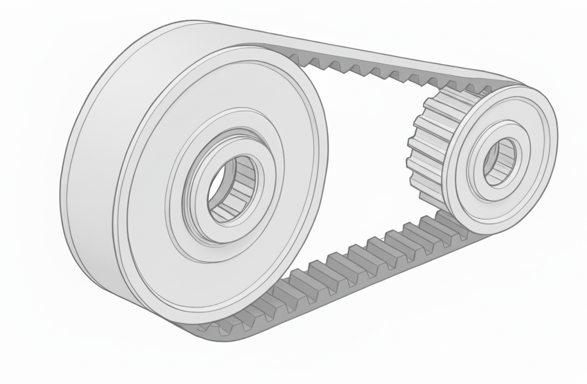
So, what are the benefits of incorporating a bearing function into a one-way clutch? For example, in timing belt drives, during the operation where the clutch slips and locks, the shaft may rotate in the slipping direction, causing power to be transmitted. Specifically, when the radial load imposed by the belt is around 0 to 320g, the clutch locks and slips. However, if the load exceeds this range, the shaft is dragged along, and the clutch fails to perform its intended function. Thus, when belt tension is applied, locking failures occur due to radial loads from the belt tension acting on the clutch section. Additionally, the friction between the shaft and bearing section increases as radial loads from the belt tension act on the bearing section, causing the shaft to be driven along.
The root cause lies in the friction generated because the shaft is supported by resin. In contrast, a structure using ball bearings to absorb radial loads eliminates unnecessary friction, allowing the one-way clutch to reliably perform its intended function. In other words, even when belt tension is applied or when the one-way clutch is integrated into a gear train, a one-way clutch bearing incorporating ball bearings will operate correctly without issues. However, when radial loads are not that strong, a plastic plain bearing is also acceptable. Incorporating a plain bearing reduces damage to the shaft compared to relying solely on the meshing rollers for support and also minimizes wear on other components. As a result, wear particles accumulate less inside the clutch, enabling reliable locking operation.
 Summary of What is a One-way Clutch Bearing?
Summary of What is a One-way Clutch Bearing?
This time, we explained the differences and mechanisms between one-way clutches and one-way clutch bearings, as well as the reason for incorporating bearing functions. When a bearing is built into a one-way clutch, friction is minimized, allowing the clutch to function reliably without issues. TOK's one-way clutches incorporate bearings, enabling them to perform locking operations dependably.
View TOK's product information here.